The key benefits of these models can be broadly classified as :
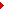 Visualising the Anatomy : The models provide a very close-to-real information about the condition of the particular anatomical region at the time of scanning. This can be useful for pre-operative planning, communication between professionals of multiple disciplines and for teaching at institutes or special workshops
Visualising the Anatomy : The models provide a very close-to-real information about the condition of the particular anatomical region at the time of scanning. This can be useful for pre-operative planning, communication between professionals of multiple disciplines and for teaching at institutes or special workshops
 Surgery Rehearsals : These models serve as useful dummies for rehearsing the surgical procedures. These can be cut &/or joined in various combinations to verify and ensure that the final result is as expected by the surgeon.
Surgery Rehearsals : These models serve as useful dummies for rehearsing the surgical procedures. These can be cut &/or joined in various combinations to verify and ensure that the final result is as expected by the surgeon.
 Developing Custom Implants : As the CT or MRI scan provides very accurate data on the anatomy, the implant developed based on it will also be highly accurate. The ability of making mirrored models on the computer itself, adds to the variousossibilities of working.
Developing Custom Implants : As the CT or MRI scan provides very accurate data on the anatomy, the implant developed based on it will also be highly accurate. The ability of making mirrored models on the computer itself, adds to the variousossibilities of working.

